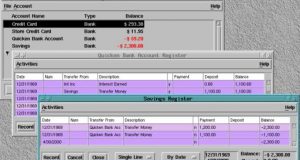
Ralph Krause Issue #76, August 2000 We continually hear “I would only use Linux except I need to …”. One of those missing pieces has been to run Quicken. Find out what programs are available for Linux that offer an alternative to Quicken. As Linux finds its way onto more and more computers, the need for a broader range of ...
Read More »Linux Magazine
Yellow Dog Linux on the iMac
Stew Benedict Issue #76, August 2000 A guide to installing and running YDL on a power PC. First, a disclaimer: I’m not a fanatic Macintosh guy. I got a Macintosh late in my computing career, just last year in fact—an iMac. I was working on a cross-platform Tcl/Tk project, and I was getting pretty involved in fine-tuning the GUI for ...
Read More »LinuxPPC on the Macintosh PowerBook
Richard Kinne Issue #76, August 2000 Graphical installation environments help Macintosh play better than ever with Linux. To say Linux has undergone a growth in popularity over the last few years is, of course, an understatement. One cannot read any computer-related medium today without being bombarded with news and views on the Linux operating system. Some would even have you ...
Read More »A GNU/Linux Wristwatch Videophone
Steve Mann Issue #75, July 2000 This fully fuctioning prototype, designed and built by Steve Mann in 1998, was demonstrated in 1999, and later used to deliver a videoconference at ISSCC 2000. Videophone wristwatches are a science-fiction concept that is here today. The two key inventive concepts that make this new technology possible are: The use of a body-worn computer ...
Read More »THOR: A Versatile Commodity Component of Supercomputer Development
Robert A. Davis Issue #75, July 2000 CERN continues to use Linux as their OS of choice for modeling and simulation studies. The world’s highest energy particle accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), is presently being constructed at the European Center for Particle Physics Research (CERN) near Geneva, Switzerland. The planned date for first collisions is 2005. Since the demise ...
Read More »Linux kernel and the GNU tools
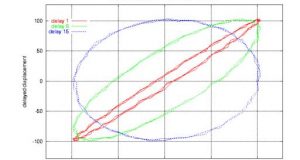
Juergen Kahrs Issue #75, July 2000 All that is real is reasonable, and all that is reasonable is real. —G.W.F. Hegel, 1770-1831 Scientists and engineers were among the first to notice what a powerful combination the Linux kernel and the GNU tools are. Thus, it is no surprise that it was the sober scientists who started replacing expensive supercomputers with ...
Read More »Tracking Satellites with PREDICT
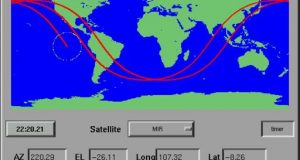
John A. Magliacane Issue #75, July 2000 A look at the development and use of an open-source satellite-tracking and orbital-prediction program. When Sputnik 1 was launched into orbit on October 4, 1957, the space age was born and the fields of science, engineering and technology were changed forever. At last count, there were over 8500 payloads from over 30 countries ...
Read More »Gri: A Language for Scientific Illustration
Dan E. Kelley Peter S. Galbraith Issue #75, July 2000 This scripting language avoids integrating analysis and display capabilities and instead focuses on providing precise and flexible control over the display of technical material. Like other computer users, scientists sometimes find themselves torn between simple tools and complex tools, between ease of use and power. Take writing, for example. The ...
Read More »Parametric Modelling: Killer Apps for Linux Clusters
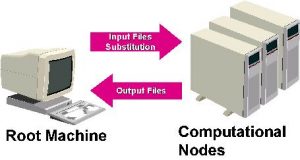
David Abramson Issue #73, May 2000 Get ready for parallel processing with the University of Michigan. After nearly 20 years of research and development, there still has not been a wide-scale uptake of parallel computing technology. However, with recent advances in PC-based hardware and networking products, it is now possible to build a parallel computer from industry-standard, commercial, off-the-shelf products. ...
Read More »X/Motif Programming
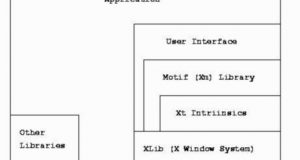
Ibrahim F. Haddad Issue #73, May 2000 And God said “Let there be light”! This article will introduce the basic concepts in building a graphical user interface in X and Motif. I’ll go into a quick introduction to the X Window System and its programming model, then introduce Motif and illustrate some concepts with a sample program. Finally, we’ll go ...
Read More » Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India
Linux, Linux OS, Free Linux Operating System, Linux India Linux, Linux OS,Free Linux Operating System,Linux India supports Linux users in India, Free Software on Linux OS, Linux India helps to growth Linux OS in India